Basics of HTML, CSS & JS
![]()
Html Text
- HTML elements are used to describe the structure of the page (e.g. headings, subheadings, paragraphs).
- They also provide semantic information (e.g. where emphasis should be placed, the definition of any acronyms used, when given text is a quotation).
how to add markup to the text that appears on your pages :
-
Structural markup: the elements that you can use to describe both headings and paragraphs
-
Semantic markup: which provides extra information; such as where emphasis is placed in a sentence, that something you have written is a quotation (and who said it), the meaning of acronyms, and so on .
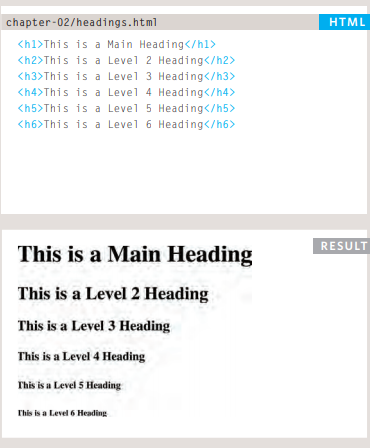
## Headings
## paragraphs To create a paragraph, surround the words that make up the paragraph with an opening < p > tag and closing < p > tag.

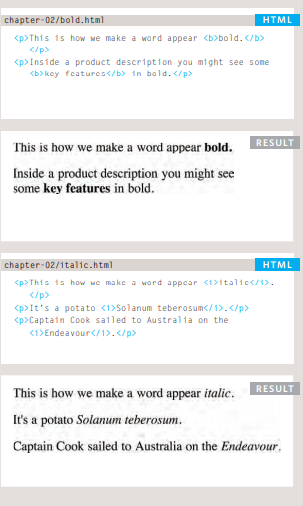
Bold & Italic
-
< b > : By enclosing words in the tags < b > and < /b > we can make characters appear bold.The < b > element also represents a section of text that would be presented in a visually different way (for example key words in a paragraph) although the use of the < b > element does not imply any additional meaning
-
< i >: By enclosing words in the tags < i > and < /i> we can make characters appear italic.The < i > element also represents a section of text that would be said in a different way from surrounding content — such as technical terms, names of ships, foreign words, thoughts, or other terms that would usually be italicized
Superscript & SubscripT
- < sup > :
The < sup > element is used to contain characters that should be superscript such as the suffixes of dates or mathematical concepts like raising a number to a power such as 2^2.
- < sub > :
The < sub> element is used to contain characters that should be subscript. It is commonly used with foot notes or chemical formulas such as H2O .

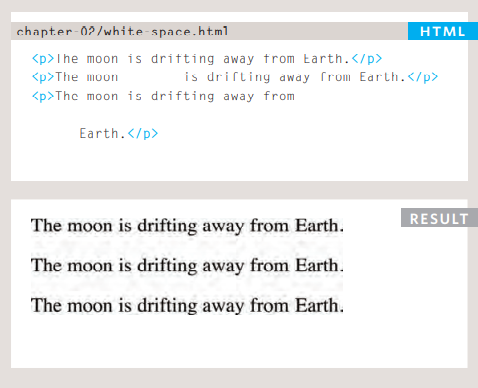
White Space
Line Breaks & Horizontal Rules
-
< br /> As you have already seen, the browser will automatically show each new paragraph or heading on a new line. But if you wanted to add a line break inside the middle of a paragraph you can use the line break tag < br / >.
-
< hr /> To create a break between themes — such as a change of topic in a book or a new scene in a play — you can add a horizontal rule between sections using the < hr / > tag.
OTHERS TEXT TAGS
- Changes to CONTENT < ins> , < del> , < s>
- Author Details < address>
- Citations & Definitions < cite> , < dfn>
- Abbreviations & Acronyms < abbr>
- Quotations < blockquote> , < q>
- Strong & Emphasis < strong> < em>
Introducing CSS
CSS Associates Style rules with HTML elements
- CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
-
Rules are made up of selectors (that specify the elements the rule applies to) and declarations (that indicate what these elements should look like).
-
Different types of selectors allow you to target your rules at different elements.
-
Declarations are made up of two parts: the properties of the element that you want to change, and the values of those properties. For example, the font-family property sets the choice of font, and the value arial specifies Arial as the preferred typeface.
- CSS rules usually appear in a separate document, although they may appear within an HTML page

Basic javascript instructures
- A script is made up of a series of statements. Each statement is like a step in a recipe.
- Scripts contain very precise instructions. For example, you might specify that a value must be remembered before creating a calculation using that value.
- Variables are used to temporarily store pieces of information used in the script.
- Arrays are special types of variables that store more than one piece of related information.
- JavaScript distinguishes between numbers (0-9),strings (text), and Boolean values (true or false).
- Expressions evaluate into a single value.
- Expressions rely on operators to calculate a value
Decisions and loops
- Conditional statements allow your code to make decisions about what to do next.
-
Comparison operators (===, ! ==, ==, ! =, <, >, <=, =>) are used to compare two operands.

-
Logical operators allow you to combine more than one set of comparison operators.
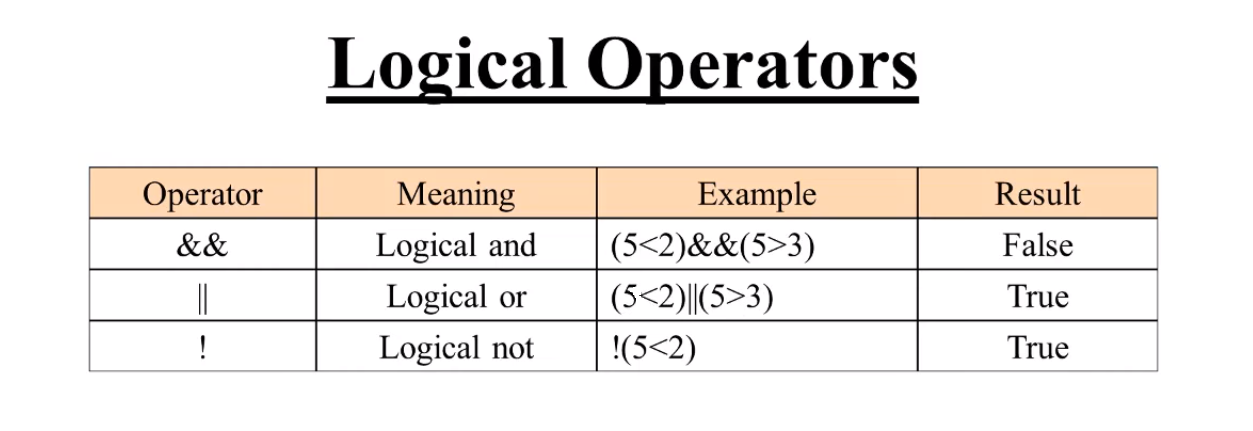
-
if … else statements allow you to run one set of code if a condition is true, and another if it is false.
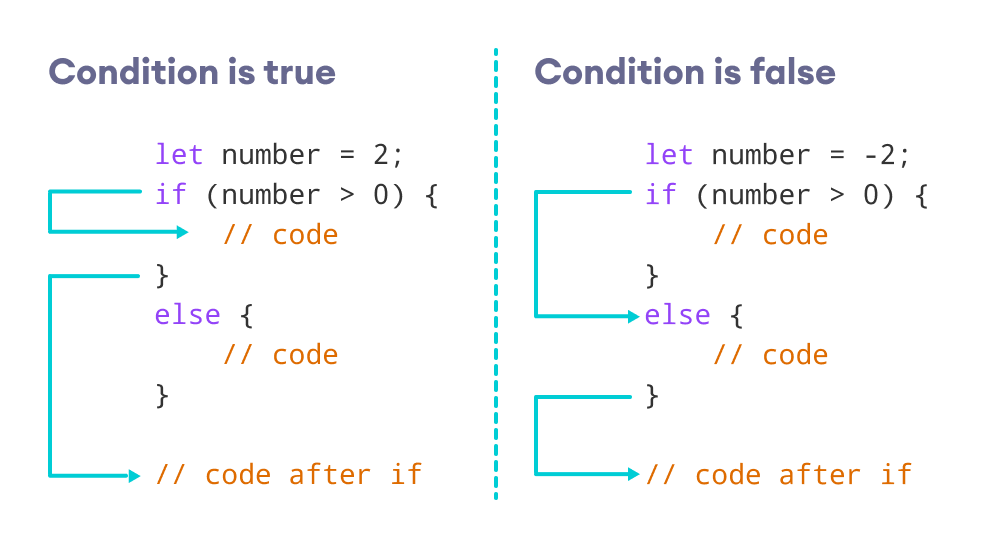
- switch statements allow you to compare a value against possible outcomes (and also provides a default option if none match).

