Object-Oriented Programming, HTML Tables

Domain Modeling
 Domain modeling is the process of creating a conceptual model in code for a specific problem. A model describes the various entities, their attributes and behaviors, as well as the constraints that govern the problem domain. An entity that stores data in properties and encapsulates behaviors in methods is commonly referred to as an object-oriented model.
Domain modeling is the process of creating a conceptual model in code for a specific problem. A model describes the various entities, their attributes and behaviors, as well as the constraints that govern the problem domain. An entity that stores data in properties and encapsulates behaviors in methods is commonly referred to as an object-oriented model.
A domain model that’s articulated well can verify and validate the understanding of a specific problem among various stakeholders. As a communication tool, it defines a vocabulary that can be used within and between both technical and business teams.
- Domain modeling is the process of creating a conceptual model for a specific problem. And a domain model that’s articulated well can verify and validate your understanding of that problem.
Here’s some tips to follow when building your own domain models.
-
When modeling a single entity that’ll have many instances, build self-contained objects with the same attributes and behaviors.
- Model its attributes with a constructor function that defines and initializes properties.
- Model its behaviors with small methods that focus on doing one job well.
- Create instances using the new keyword followed by a call to a constructor function.
- Store the newly created object in a variable so you can access its properties and methods from outside.
- Use the this variable within methods so you can access the object’s properties and methods from inside.
HTML Tables :
HTML tables allow web developers to arrange data into rows and columns.
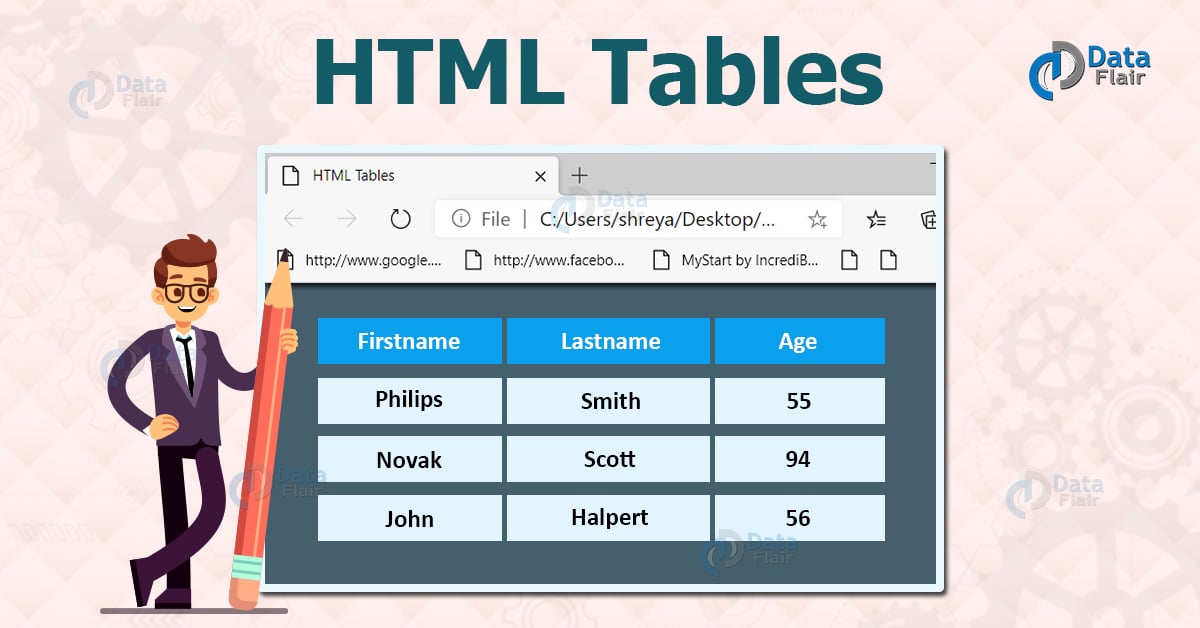
Define an HTML Table :
-
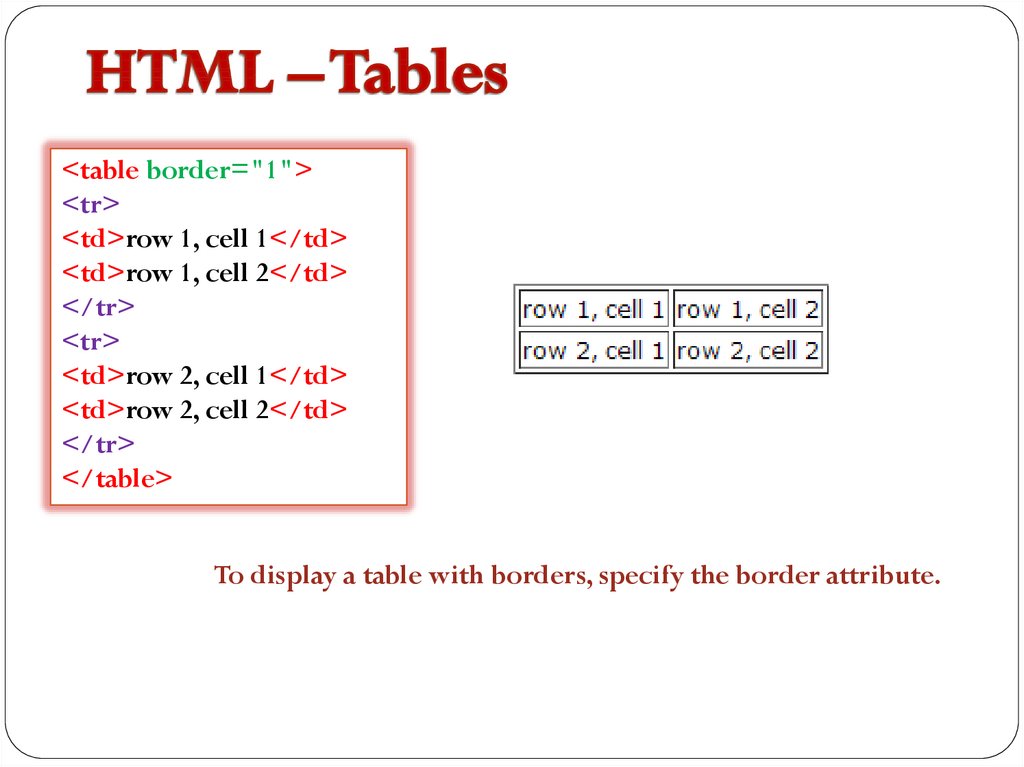
The < table> tag defines an HTML table.
-
Each table row is defined with a < tr> tag. Each table header is defined with a <th> tag. Each table data/cell is defined with a < td> tag.
-
By default, the text in < th> elements are bold and centered.
-
By default, the text in < td> elements are regular and left-aligned.
-
Note: The <td> elements are the data containers of the table. They can contain all sorts of HTML elements; text, images, lists, other tables, etc.
HTML Table - Add a Border :
To add a border to a table, use the CSS border property:
table, th, td { border: 1px solid black; }
HTML Table - Collapsed Borders :
To let the borders collapse into one border, add the CSS border-collapse property
table, th, td { border: 1px solid black; border-collapse: collapse; }
HTML Table - Add Cell Padding :
-
Cell padding specifies the space between the cell content and its borders.
-
If you do not specify a padding, the table cells will be displayed without padding.
-
To set the padding, use the CSS padding property
th, td { padding: 15px; }
HTML Table - Left-align Headings :
-
By default, table headings are bold and centered.
-
To left-align the table headings, use the CSS text-align property
th { text-align: left; }
Summary
- Use the HTML < table> element to define a table
- Use the HTML < tr> element to define a table row
- Use the HTML < td> element to define a table data
- Use the HTML < th> element to define a table heading
- Use the HTML < caption> element to define a table caption
- Use the CSS border property to define a border
- Use the CSS border-collapse property to collapse cell borders
- Use the CSS padding property to add padding to cells
- Use the CSS text-align property to align cell text
- Use the CSS border-spacing property to set the spacing between cells
- Use the colspan attribute to make a cell span many columns
- Use the rowspan attribute to make a cell span many rows
- Use the id attribute to uniquely define one table
JS Functions, Methods, and Objects
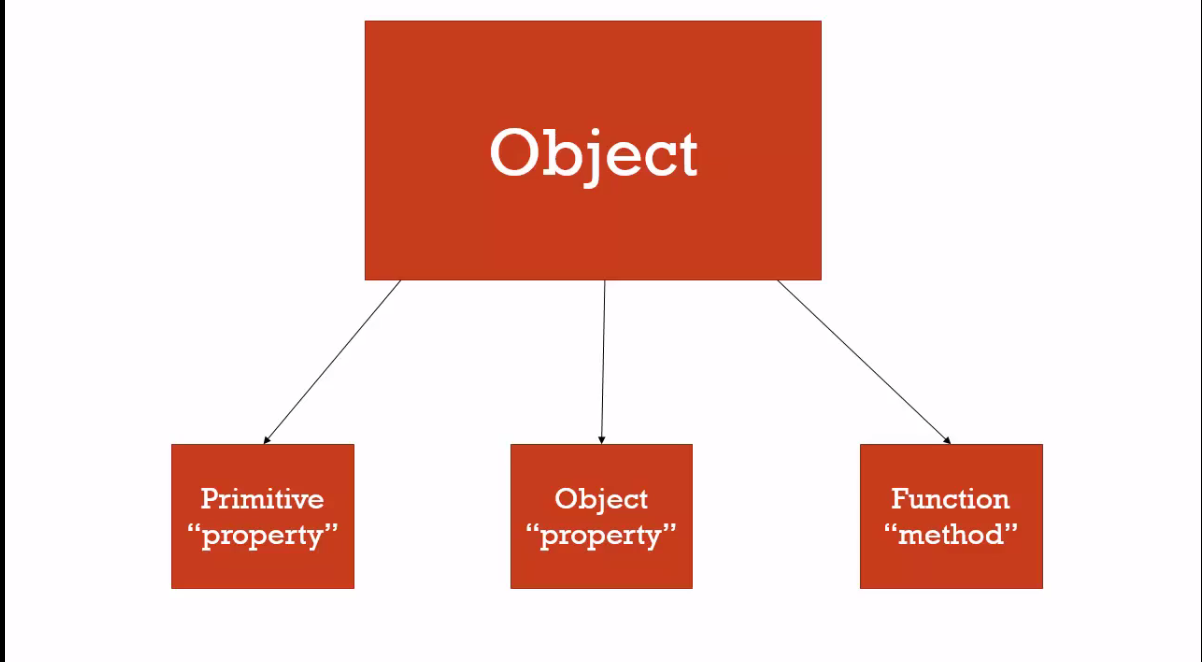
JavaScript Object Properties :
Properties are the most important part of any JavaScript object.
JavaScript Properties
Properties are the values associated with a JavaScript object.
A JavaScript object is a collection of unordered properties.
Properties can usually be changed, added, and deleted, but some are read only.
1. Accessing JavaScript Properties
The syntax for accessing the property of an object is:
objectName.property // person.age or
objectName[” property”] // person[” age”] or
objectName[ expression] // x = “age”; person[ x]
2. JavaScript for…in Loop
The JavaScript for…in statement loops through the properties of an object.
- Syntax :
for (variable in object) { // code to be executed } The block of code inside of the for…in loop will be executed once for each property
3. Adding New Properties
You can add new properties to an existing object by simply giving it a value.
Assume that the person object already exists - you can then give it new properties:
Example : person.nationality = “English”;
4. Deleting Properties
The delete keyword deletes a property from an object:
Example : let person = {firstName:”John”, lastName:”Doe”, age:50, eyeColor:”blue”}; delete person.age; // or delete person[” age”];
5. Property Attributes
All properties have a name. In addition they also have a value.
The value is one of the property’s attributes.
Other attributes are: enumerable, configurable, and writable.
These attributes define how the property can be accessed (is it readable?, is it writable?)
In JavaScript, all attributes can be read, but only the value attribute can be changed (and only if the property is writable).
JavaScript Object Methods
The this Keyword
In a function definition, this refers to the “owner” of the function.
In other words, this.firstName means the firstName property of this object.
JavaScript Methods
-
JavaScript methods are actions that can be performed on objects.
-
A JavaScript method is a property containing a function definition.
Property : Value fullName function() {return this.firstName + “ “ + this.lastName;}
Accessing Object Methods
You access an object method with the following syntax:
objectName.methodName()
-
You will typically describe fullName() as a method of the person object, and fullName as a property.
-
The fullName property will execute (as a function) when it is invoked with ().
