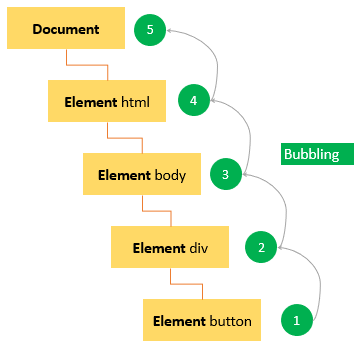
# Forms and JS Events :
# HTML Forms :
An HTML form is used to collect user input. The user input is most often sent to a server for processing.

-
The < form> Element
The HTML < form> element is used to create an HTML form for user input:
< form> . form elements . < /form>
The < form> element is a container for different types of input elements, such as: text fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, submit buttons, etc.
-
The < input> Element
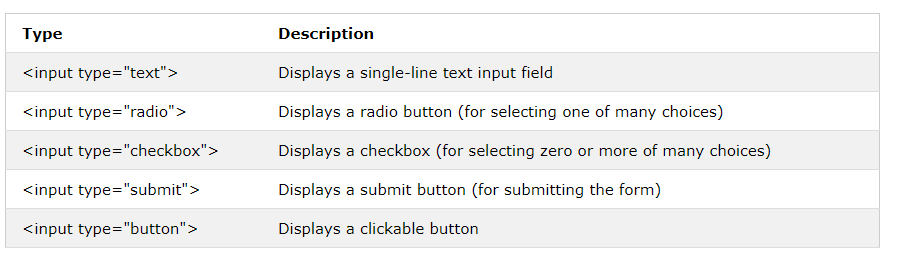
The HTML < input> element is the most used form element.
An < input> element can be displayed in many ways, depending on the type attribute.
-
Text Fields
The defines a single-line input field for text input.
-
The < label> Element
The < label> tag defines a label for many form elements.
The < label> element is useful for screen-reader users, because the screen-reader will read out loud the label when the user focus on the input element.
The < label> element also help users who have difficulty clicking on very small regions (such as radio buttons or checkboxes) - because when the user clicks the text within the < label> element, it toggles the radio button/checkbox.
The for attribute of the < label> tag should be equal to the id attribute of the < input> element to bind them together.
-
Radio Buttons
The < input type=”radio”> defines a radio button.
Radio buttons let a user select ONE of a limited number of choices.

-
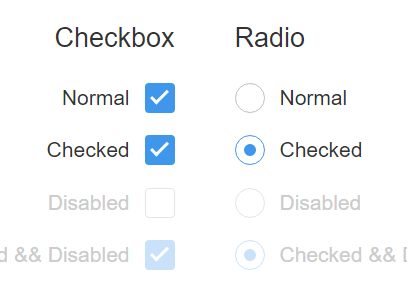
Checkboxes
The < input type=”checkbox”> defines a checkbox.
Checkboxes let a user select ZERO or MORE options of a limited number of choices.
-
The Submit Button
The < input type=”submit”> defines a button for submitting the form data to a form-handler.
The form-handler is typically a file on the server with a script for processing input data.
The form-handler is specified in the form’s action attribute.

-
The Name Attribute for < input>
Notice that each input field must have a name attribute to be submitted.
If the name attribute is omitted, the value of the input field will not be sent at all.
LISTS, TABLES AND FORMS
-
List markers can be given different appearances using the list-style-type and list-style image properties.
-
Table cells can have different borders and spacing in different browsers, but there are properties you can use to control them and make them more consistent.
-
Forms are easier to use if the form controls are vertically aligned using CSS.
-
Forms benefit from styles that make them feel more interactive
Events

HTML events are “things” that happen to HTML elements.
When JavaScript is used in HTML pages, JavaScript can “react” on these events.
HTML Events
An HTML event can be something the browser does, or something a user does.
Here are some examples of HTML events:
- An HTML web page has finished loading
- An HTML input field was changed
- An HTML button was clicked
Often, when events happen, you may want to do something.
JavaScript lets you execute code when events are detected.
HTML allows event handler attributes, with JavaScript code, to be added to HTML elements.
With single quotes:
< element event=’some JavaScript’>
With double quotes:
< element event=”some JavaScript”>
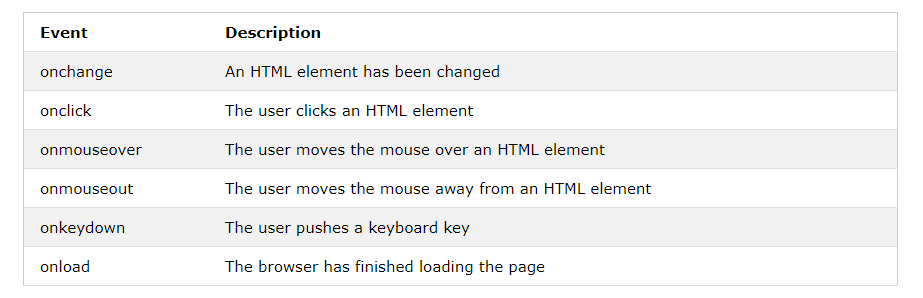
Common HTML Events
Here is a list of some common HTML events:
What can JavaScript Do?
Event handlers can be used to handle and verify user input, user actions, and browser actions:
- Things that should be done every time a page loads
- Things that should be done when the page is closed
- Action that should be performed when a user clicks a button
- Content that should be verified when a user inputs data And more …
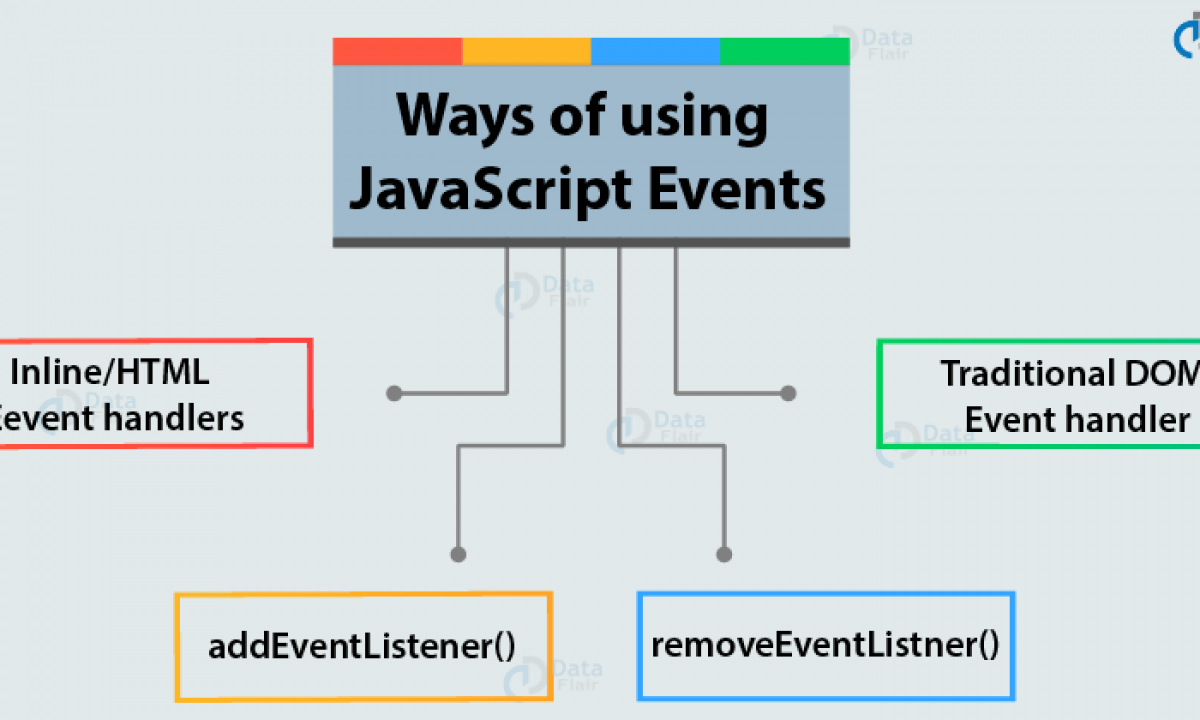
Many different methods can be used to let JavaScript work with events:
- HTML event attributes can execute JavaScript code directly
- HTML event attributes can call JavaScript functions
- You can assign your own event handler functions to HTML elements
- You can prevent events from being sent or being handled And more …