State and Props
React: Component Lifecycle Events
What are component lifecycle events?
React lets you define components as classes or functions. The methods that you are able to use on these are called lifecycle events. These methods can be called during the lifecycle of a component, and they allow you to update the UI and application states.
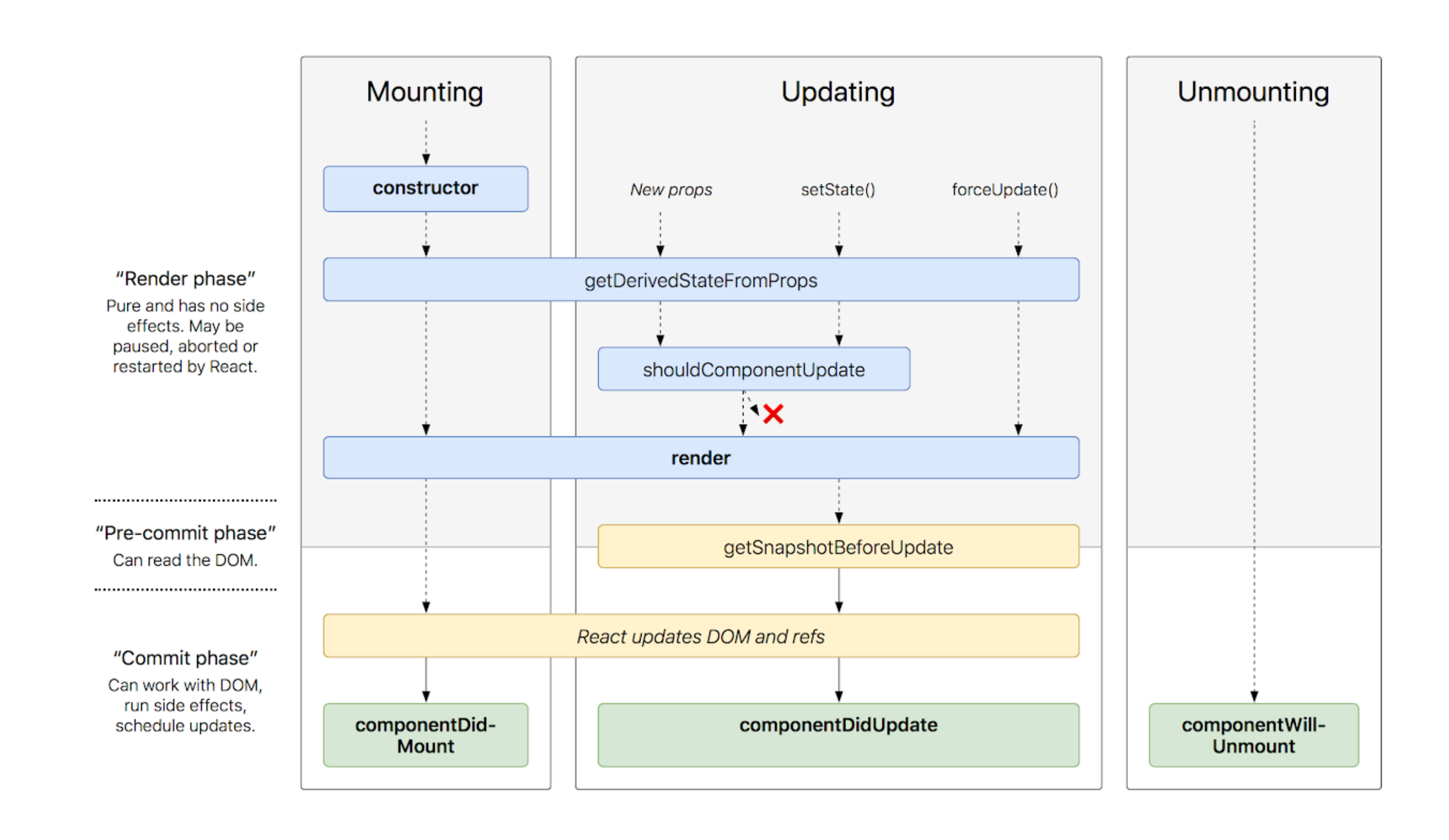
Based off the diagram, what happens first, the ‘render’ or the ‘componentDidMount’?
componentDidMount
What is the very first thing to happen in the lifecycle of React?
Mounting :
When an instance of a component is being created and inserted into the DOM it occurs during the mounting phase. Constructor, static getDerivedStateFromProps, render, componentDidMount, and UNSAFE_componentWillMount all occur in this order during mounting.
Put the following things in the order that they happen: componentDidMount, render, constructor, componentWillUnmount, React Updates
-
constructor
-
render
-
React Updates
-
componentDidMount
-
componentWillUnmoun
What does componentDidMount do?
This method is invoked immediately after a component is mounted. If you need to load anything using a network request or initialize the DOM, it should go here. This method is a good place to set up any subscriptions. If you do that, don’t forget to unsubscribe in componentWillUnmount().
React State Vs Props

What types of things can you pass in the props?
## Props (aka “properties”) in React allows us to pass values from a parent component down to a child component. The values can be any data type, from strings to functions, objects, etc
## What is the big difference between props and state?
## In a React component, props are variables passed to it by its parent component. State on the other hand is still variables, but directly initialized and managed by the component. The state can be initialized by props. ## so, Props are used to pass data, whereas state is for managing data. Data from props is read-only, and cannot be modified by a component that is receiving it from outside. State data can be modified by its own component, but is private (cannot be accessed from outside).
## When do we re-render our application?
## React components automatically re-render whenever there is a change in their state or props. A simple update of the state, from anywhere in the code, causes all the User Interface (UI) elements to be re-rendered automatically.
What are some examples of things that we could store in state?
A store is basically just a plain JavaScript object that allows components to share state. In a way, we can think of a store as a database. On the most fundamental level, both constructs allow us to store data in some form or another

Things I want to know more about
I want to knpw more about the differences between state and props also i want to know and learn about store and redux.