useState() Hook
Review, Research, and Discussion
How does React differ from vanilla JS/HTML/CSS?
-
Vanilla JS requires a lot of typing : JS requires a lot of codes so would be little messy and that make it less efficient than React.
-
React JS is for code organization :ReactJs is great for organizing the code. as you can see all the above code is on one page, script.js.
-
React :A JavaScript library for building user interfaces. Lots of people use React as the V in MVC. Since React makes no assumptions about the rest of your technology stack, it’s easy to try it out on a small feature in an existing project.
-
What is the primary difference between a function component and a class component?
-
Functional components are basic JavaScript functions. These are typically arrow functions but can also be created with the regular function keyword.
-
React lifecycle methods (for example, componentDidMount) cannot be used in functional components.
-
There is no render method used in functional components.
-
Functional components can accept and use props.
-
Functional components should be favored if you do not need to make use of React state.
-
Class components make use of ES6 class and extend the Component class in React.
-
Sometimes called “smart” or “stateful” components as they tend to implement logic and state.
-
React lifecycle methods can be used inside class components (for example, componentDidMount).
-
You pass props down to class components and access them with this.props.
Document the following Vocabulary Terms
Functional Components : basic JavaScript functions. These are typically arrow functions but can also be created with the regular function keyword. Sometimes referred to as “dumb” or “stateless” components as they simply accept data and display them in some form; that is they are mainly responsible for rendering UI.
Children / Child Components : children is a special property of React components which contains any child elements defined within the component
Preparation Materials
Hooks let us organize the logic inside a component into reusable isolated units , we used to avoid Huge components , Duplicated logic , Complex patterns .
-
Hooks let you always use functions instead of having to constantly switch between functions, classes, higher-order components, and render props.
-
Hooks are functions that let you “hook into” React state and lifecycle features from function components
-
useState
const [count, setCount] = useState() is similar to this.state.count and this.setState in a class
-
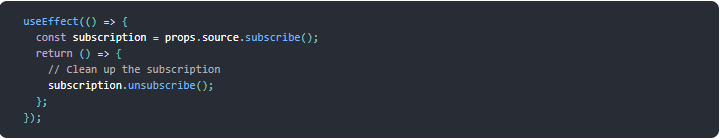
useEffect
-
Hooks are JavaScript functions, but they impose two additional rules:
- Only call Hooks at the top level. Don’t call Hooks inside loops, conditions, or nested functions.
- Only call Hooks from React function components. Don’t call Hooks from regular JavaScript functions.
useContext
lets you subscribe to React context without introducing nesting
-
useReducer
lets you manage local state of complex components with a reducer
-
Basic Hooks
useState

useEffect
useContext
useReducer useCallback useMemo useRef useImperativeHandle useLayoutEffect useDebugValue
Resources

