Hash Tables
Terminology
Hash
-
an algorithm takes a string and converts it into a value that could be used for security or some other purpose
-
in a hashtable, it is used to determine the index of the array
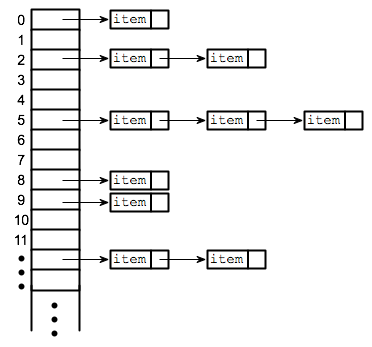
Buckets
-
contained in each index of the array of the hashtable
-
Each index is a bucket
-
index could potentially contain multiple key/value pairs if a collision occurs
Collisions
-
what happens when more than one key gets hashed to the same location of the hashtable
Hashing is implemented in two steps:
-
An element is converted into an integer by using a hash function. This element can be used as an index to store the original element, which falls into the hash table.
-
The element is stored in the hash table where it can be quickly retrieved using hashed key.
hash = hashfunc(key)
index = hash % array_size
What are Hash Tables
-
a data structure that utilizes key value pairs
-
every Node or Bucket has both a key, and a value
-
basic idea of a hashtable is the ability to store the key and quickly retrieve the value through a hash
-
hash is the ability to encode the key that will eventually map to a specific location
-
in the data structure, we can directly retrieve the value
-
O(1) time complexity for lookups
Internal Methods
Add()
-
send the key to the GetHash method
-
determine the index of where it should be placed
-
go to that index
-
Check if something exists at that index already
-
if it doesn’t, add it with the key/value pair.
-
else add the new key/value pair to the data structure within that bucket
Find()
-
takes in a key
-
gets the Hash
-
goes to the index location specified
Contains()
-
accept a key
-
return a boolean if that key exists inside the hashtable
GetHash()
-
GetHash will accept a key as a string
-
conduct the hash
-
return the index of the array where the key/value should be placed