How Javascript makes Web pages More interactive !!
## 1. ACCESS CONTENT * You can use JavaScript to select any element, attribute, or text from an HTML page. For example:*
- Select the text inside all of the
elements on a page - Select any elements that have a c 1 ass attribute with a value of note
- Find out what was entered into a text input whose id attribute has avalue of ema i
2. MODIFY CONTENT
You can use JavaScript to add elements, attributes, and text to the page, or remove them. For example:
- Add a paragraph of text after the first
element - Change the value of c 1 ass attributes to trigger new CSS rules for those elements
- Change the size or position of an element
3. PROGRAM RULES
You can specify a set of steps for the browser to follow (like a recipe), which allows it to access or change the content of a page. For example:
- A gallery script could check which image a user clicked on and display a larger version of that image.
- A mortgage calculator could collect values from a form, perform a calculation, and display repayments.
- An animation could check the dimensions of the browser window and move an image to the bottom of the viewable area (also known as the viewport).
4.
REACT TO EVENTS You can specify that a script should run when a specific event has occurred. For example, it could be run when:
- A button is pressed
- A link is clicked (or tapped) on
- A cursor hovers over an element
- Information is added to a form
- An interval of time has passed
- A web page has finished loading
What is the script and how can I creat one ?
-
A script is a series of instructions that the computer can follow in order to achieve a goal.
- Each time the script runs, it might only use a subset of all the instructions.
- Computers approach tasks in a different way than humans, so your instructions must let the computer solve the task prggrammatically.
- To approach writing a script, break down your goal into a series of tasks and then work out each step needed to complete that task (a flowchart can help).
EXPRESSIONS:
An expression evaluates into (results in) a single value. Broadly speaking there are two types of expressions :
** 1. EXPRESSIONS THAT JUST ASSIGN A VALUE TO A VARIABLE In order for a variable **
to be useful, it needs to be given a value. As you have seen, this is done using the assignment operator (the equals sign). var color = ‘beige’;
When you first declare a variable using the var keyword, it is given a special value of undefined. This will change when you assign a value to it. Technically,undefined is a data type like a number, string, or Boolean.
** 2. EXPRESSIONS THAT USE TWO OR MORE VALUES TO RETURN A SINGLE VALUE ** You can perform operations on any number of individual values to determine a single value.
example: var area = 3 * 2; The value of area is now 6. Here the expression 3 * 2 evaluates into 6. This example also uses the assignment operator, so the result of the expression 3 * 2 is stored in the variable called area.
OPERATORS
**Expressions rely on things called operators; they allow programmers to create a single value from one or more values **
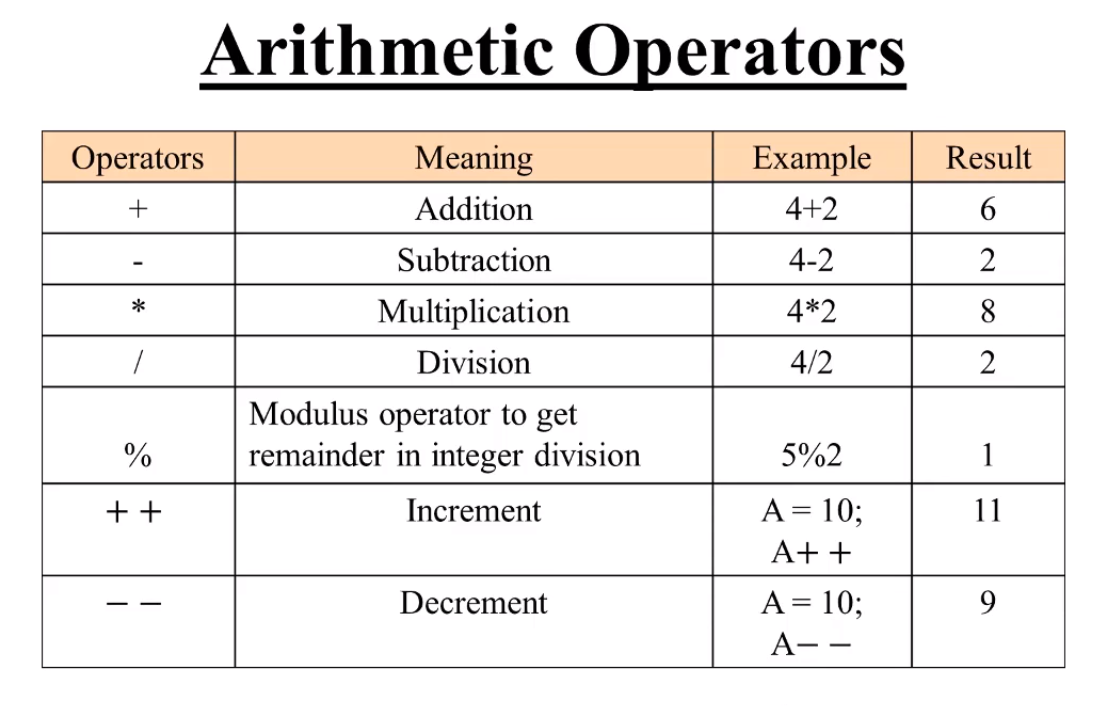
**1. ARITHMETI C OPERATORS ** JavaScript contains the following mathematical operators :
2. STRING OPERATOR There is just one string operator: the+ symbol. It is used to join the strings on either side of it.
function
WHAT IS A FUNCTION? Functions let you group a series of statements together to perform a specific task. If different parts of a script repeat the same task, you can reuse the function (rather than repeating the same set of statements).
JavaScript Function Syntax :
function name(parameter1, parameter2, parameter3) { // code to be executed }
Calling a function
name();
Why Functions?
-
You can reuse code: Define the code once, and use it many times.
-
You can use the same code many times with different arguments, to produce different results.
